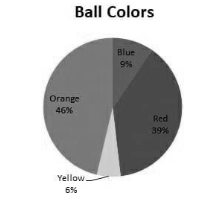
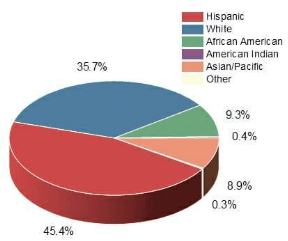
A pie chart is a visual representation of data in the shape of a circular chart or pie, with the slices indicating the magnitude of the data. To represent data in the shape of a pie chart, you’ll need a list of numerical and categorical variables. Each slice’s arc length, and hence its area and centre angle in a pie chart, is proportionate to the quantity it depicts.
Definition of Pie Chart
A pie chart is a type of graph that records data in a circular shape and divides it into sectors to represent data from a single component of the whole. Each of these sectors or slices represents a proportionate component of the whole. Pie charts, often known as pie diagrams, help with data interpretation and display. It can be used to compare data as well.
Types of Pie Charts
Pie charts are classified into two types based on the graph’s dimension: a 2D pie chart and a 3D pie chart.
2D Pie Chart
A circular graph depicting the percentage of variables in a dataset is known as a two-dimensional pie chart. This type of pie chart displays the items in two dimensions. The 2D pie chart is classified into four types based on how the variables are visualised on the pie chart:
- Simple Pie Chart
- Exploded Pie Chart
- Pie of Pie
- Bar of Pie
3D Pie Chart
A three-dimensional version of a pie chart is known as a 3D pie chart. It’s mostly for show, and it has nothing to do with how data is displayed in a pie chart. Instead, it distorts the graph and makes it harder to understand. The three-dimensional pie chart is split into two sections:
- A simple 3D chart
- exploded 3D chart
Interpret the key Results for Pie Chart
To compare the proportion of data in each category, use a pie chart. A pie chart is a circle (the pie) cut into slices (the slices) to depict the proportion of observations in each category.
To interpret a pie chart, compare groups.
- When evaluating a pie chart, look for differences in the size of the slices. The size of a slice represents the proportion of observations in each group.
- When comparing many pie charts, check for differences in slice size for the same categories across all of them.
The proportions of job classifications at a corporation are depicted in the pie chart below. Manufacturing takes up the most space. Sales and marketing positions are roughly equal in number. The janitorial portion is the smallest.
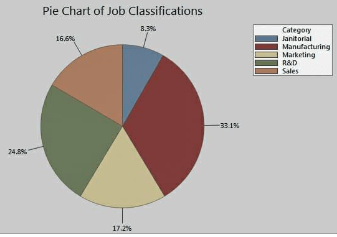
Directions: Examine the pie chart below and respond to the questions that follow
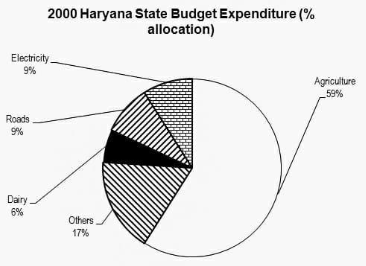
Example 1: In the centre angle of the sector for agriculture expenditure, how many degrees should there be?
- 220
- 213
- 210
- 208
In a pie chart, 100 percent is distributed over 360 degrees. As a result, 1 percent equals 3.6°. Agriculture spending accounts for 59% of total spending. As a result, 3.6 59 = 212.4°. The solution is (2)
Example 2: What is the approximate ratio of agricultural to dairy expenditures?
- 8:3
- 9:2
- 70:1
- 10:1
Sol: One common blunder here is that students calculate the actual agricultural and dairy values. Because budget spending is proportional to the area covered, the ratio of agriculture to dairy spending would be the ratio of matching percent allocations. Agriculture/Dairy = 59/6 = 10/1 as a result. The solution is (4).
Example 3: In Haryana, a total of Rs. 120 million was spent in 2000. What was the amount of money spent on roads by the Haryana government?
- 15.4
- 20
- 10.8
- 12
Solved: Total spending = 100% = Rs. 120 mn.. Road expenditure = 9% = 9/100 x 120 = Rs. 10.8 mn. As a result, the answer is 3rdoption.
Example 4: If Rs. 9 mn was spent on dairy in 2000, what was the total expenditure in million?
- 150
- 140
- 160
- 130
Sol: Dairy took 9 mn. In the year 2000, this sum accounted for 6% of total expenditure.
6 = (Dairy Spending/Total Spending) / 100
100 = 6 = (9/Total Expenditure)
Total Exp = Rs. 150 million (9/6) Hence, Option 1 is the correct answer.
Example 5: In 1999, Haryana spent 11% of its total expenditures on roads. “Did Haryana spend more money on roads in 1999 than it did in 2000?” says the question.
- No other information is required.
- The entire amount spent in each year must be known.
- In 1999, the exact percent age breakdown of the various costs is required.
- Make dairy spending mandatory in both years.
Sol: percent only provides a proportional representation of total quantity.
Percentage of total expenditure is meaningless unless complete expenditure is known.
As a result, in order to compare road spending in 1999 and 2000, the total amount spent must be known.
The solution is (2).
Conclusion
Finally, after reading this post, you should be able to make a pie chart in both Excel and EdrawMax. A pie chart is a visual representation of data that can be used in a variety of situations.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out