The critical path approach of project management aids in identifying days when extra time can be spent on non-essential aspects of the project. So even if there are delays in some areas, the project can still be completed on time without affecting anyone else.
What is a critical path?
A critical path is a series of interconnected actions or tasks that must be accomplished in order for the project to be finished. It is the longest path from project start to finish (i.e. the path with the longest duration). At the same time, the shortest path represents the quickest way to complete a task. The entire project will be delayed if one of the path’s operations is delayed.
By visualising tasks and activities in a network diagram, such as a Gantt chart, the critical path method (CPM) is a particularly useful tool for scheduling tasks and keeping track of activities. Activities are represented as a network of arrows connecting two event nodes in this graphic. In order to create a functioning network of events and activities, all associated activities must be properly specified. The critical path technique allows for adjustments during the project’s execution, which is one of its most significant advantages.
Flexibility Time and Float
CP is a method for reducing the risk of failure and determining where the project manager has and does not have decision-making flexibility.
In this context, a flexible decision means that some tasks can be started earlier or later without jeopardising the project’s completion date, allowing the project manager to manipulate and adjust the project schedule based on the time between the earliest start date and the latest end date of each activity. That period is more commonly referred to as “float” or “slack” than “flexibility time.” An action with float time is not included in the critical route by definition.
If an activity has one month of float time, it will not be included in the critical path if it begins after the other successors have completed or begun, unless it is required to begin earlier due to an unexpected change in project scope or other factors.
Critical Path Method Definition
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a scheduling technique that uses network analysis to anticipate job length. The CPM is a set of processes and methodologies used in complex projects to identify and sequence the activities (critical path) that have the greatest impact on the project’s due date, schedule the time required to complete them, and create the predecessor-successor link between them.
In project management, the critical path method employs network diagrams to help decision makers see how long each task will take. CPM is critical for anticipating task timelines, and project managers can use it in conjunction with activity network diagrams to:
Schedule the amount of time each task or event will take (duration).
Combine the durations of all actions into a timeline for analysis.
Determine how each activity affects the project’s progress.
Make appropriate team assignments for key tasks.
Visualizing the Critical Path with an Activity Network Diagram
As previously said, using an activity network diagram is one of the greatest strategies to assure good project planning and scheduling. Planners can more easily visualise and specify the important activity path with such a model.
Teams use network diagrams to visualise the complete work, which is divided down into interdependent tasks, and to plan their next steps. Bubbles, boxes, and arrows will aid with understanding the activities and their relationships. The diagram is created by the project manager to model the flow of activities and show the critical path specification. Each activity is identified by a code (ID) or a name, and activity pathways must be highlighted. Here’s an example:
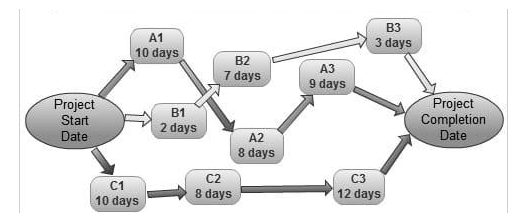
MS Excel Spreadsheet for CP Method Example
You have a complete list of all actions to be completed inside your designated project, from start to finish, in your work breakdown structure. Your objective is to determine the duration and predecessor(s) of each action before attempting to construct a network diagram. You can add activities to your critical sequence that have no float time and must be finished on time.
Spreadsheet software can be used to evaluate and visualise the critical path in project management. You can, for example, use MS Excel to construct a spreadsheet that contains all of your project activities, including their ID, duration, predecessors, and successors. MS Project, on the other hand, provides more capabilities for establishing and analysing critical routes in projects.
Conclusion
Critical path was designed with the intention of estimating work time and assisting each of these behind-schedule projects in regaining control. The critical path method is now widely used to identify the most vital tasks and ensure that your project stays on track.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




