The ability to assess, process, and mentally manipulate visual information to answer problems is known as visual reasoning. Visual reasoning is essential in the classroom and in many real-life situations. Graphs, charts, and maps require a combination of verbal, mathematical, and visual analysis to interpret the data. Visual-spatial skills are also used in everyday life, and many vocations and career pathways require these abilities as well as a strong visual memory. Even something as easy as packing bags for a vacation involves spatial thinking to picture how to position items in a suitcase to maximise storage capacity .
Reasoning Questions with Answers
Question 1: what will be in next slot 50, 45, 40, 35, 30, ?
Solution: The series’ answer is as follows .
50 – 5 = 45
45 – 5 = 40
40 – 5 = 35
35 – 5 = 30
30 – 5= 25
Hence, the correct answer is 25.
Question 2: 4096, 1024, 256, ?, 16, 4
Solution: The series’ answer is as follows .
4096 / 4 = 1024
1024 / 4 = 256
256 / 4 = 64
64 / 4 = 16
16 / 4 = 4
Hence, the correct answer is 64.
Question 3: Assuming the assertions are accurate, determine which of the two inferences is/are absolutely true, and then respond accordingly .
Statement:
T > A > H = B<=V <= U<G
Conclusion:
T > B
G > H
(1) Only conclusion I follow
(2) Either conclusion I or II follow
(3) Only conclusion II follow
(4) None Follows
(5) Both conclusion I and II follow
Solution: Given Statement: T > A > H = B<=V <= U<G
True if T > B (as T = G > U>= V>= B).
True if G > H (as H< A< T = G).
If we examine the given assertions, we can deduce that conclusion I and II are correct .
Question 4: Find out which of the findings among the given two conclusions is/are definitely true, and then give your answer based on it. In the given question, find which conclusion in the given conclusions is surely true in the given equation.
Statement:
B = K >= H = T > U <= I
Conclusion:
H > I
H ≤ I
(1) Only conclusion I follow
(2) Either conclusion I or II follow
(3) Only conclusion II follow
(4) None Follows
(5) Both conclusion I and II follow
Solution: Given Statement: B = K >= H = T > U <= I
H > I = False (as H = T > U <= I)
(as H = T > U<= I) H<= I = False
Hence, Either conclusion I or II follows.
Visual Reasoning Questions
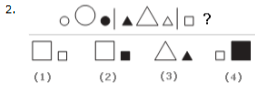
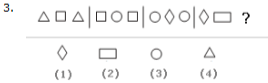
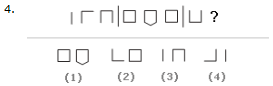
Look carefully at the sequence of symbols to find the pattern. Select the correct pattern.

A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Conclusion
Students use visual reasoning to solve problems by assessing, processing, and manipulating visual data. Students can solve difficulties by mentally recalling the relative location of objects and patterns. Providing opportunities for children to improve their spatial abilities is crucial in school and helps them manage day-to-day functions.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out