In mathematics, the full form of the term “Least Common Multiple” is “Least Common Multiple,” while the full form of “Highest Common Factor” is “the Highest Common Factor.” The highest common factor (HCF) specifies the biggest factor that exists between two or more numbers, whereas the lowest common multiple (LCM) indicates the smallest number that is exactly divisible by two or more numbers. The greatest common factor (GCF) is another name for the highest common factor (HCF), and the least common divisor is another name for the least common multiple.
The prime factorization method and the division method are two key approaches that can be used to determine the highest common factor and the lowest common multiple, respectively. Both of these approaches are ones that were taught to us in prior classes. The division method is a time-saving shortcut that can be used to determine both the H.C.F. and the L.C.M.
HCF and LCM Definition
We are well aware that the factors of a number are the same thing as the exact divisors of that number. Let’s begin with the highest common factor (H.C.F.) and work our way down to the least common multiple (L.C.M.).
HCF Definition
In mathematics, the phrase “highest common factor” is abbreviated as “HCF.”
When there are two or more positive integers, the greatest common divisor, also known as the gcd, is the largest positive integer that can be used to divide the numbers without producing a remainder. This is because the rules of mathematics require that this be the case. Take, for instance, the numbers 8 and 12: The largest common factor for the numbers 8 and 12 will be 4, as this is the biggest number that can be divided by both 8 and 12.
LCM Definition
In mathematics, the abbreviation “LCM” stands for “least common multiple.”
In mathematics, the symbol for the least common multiple (also known as the LCM) of two numbers, such as a and b, is “LCM” (a,b). The least common multiple, on the other hand, is the least positive integer that can be divided by both a and b. It is also the smallest positive integer. Take, as an illustration, the positive integers 4 and 6, for instance.
The numbers 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, and 24 are all multiples of 4.
The numbers 6, 12, 18, and 24 are all multiples of 6.
The numbers 12, 24, 36, 48, and so on all fall into the category of common multiples of 4 and 6. The number 12 would be the least frequent multiple in that group.
HCF and LCM Formula
The formula, which takes into account both the HCF and the LCM, is as follows:
Product of Two numbers = (HCF of the two numbers) x (LCM of the two numbers)
Suppose that A and B are the two numbers in question; then, according to the formula:
A x B = H.C.F.(A,B) x L.C.M.(A,B)
In terms of HCF and LCM, the formula that was just presented can also be written as follows:
H.C.F. of Two numbers = Product of Two numbers/L.C.M of two numbers
&
L.C.M of two numbers = Product of Two numbers/H.C.F. of Two numbers
How to find HCF and LCM
To determine the highest common factor and the lowest common multiple of a set of numbers, the following methods can be utilised.
- Prime factorization method
- Division method
HCF by Prime Factorisation Method
Consider the task of locating the greatest common factor among the numbers 144, 104, and 160.
Let’s start by writing down the prime factors of the numbers 144, 104, and 160.
144 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3
104 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 13
160 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 5
The common factors of 144, 104 and 160 are 2 × 2 × 2 = 8
Therefore, HCF (144, 104, 160) = 8
HCF by Division Method
Methods for calculating the HCF given any two numbers:
- Larger number/ Smaller Number
- The divisor of the above step / Remainder
- The divisor of step 2 / remainder. Keep doing this step till R = 0(Zero).
- The last step’s divisor will be HCF.
Find the highest common factor (HCF) of more than three numbers by following the methods outlined above.
LCM by Prime Factorisation Method
To determine the least common multiple of the digits 60 and 45. One method among many others for determining the least common multiple of a set of numbers is as follows:
1. Create a list beginning with the prime factors of each number.
60 = 2 × 2 x 3 × 5
45 = 3 × 3 × 5
2. After that, multiply each component by the most frequent occurrence of that factor in any number.
If the same multiple appears more than once in either of the above numbers, then multiply the factor by the number of times it appears the greatest total of times.
The incidence of Numbers in the illustration that was just presented:
2: two times
3: two times
5: one time
LCM = 2 × 2 x 3 × 3 × 5 = 180
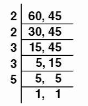
LCM by Division Method
Let’s take a look at this using the same example that we worked with earlier to determine the LCM by factoring primes.
Use the division method to find the LCM of (60,45).
Therefore, LCM of 60 and 45 = 2 × 2 x 3 × 3 × 5 = 180
Conclusion
The LCM and HCF of two or more numbers are helpful in locating quick answers and, as a result, reduce the amount of time needed for tests. In order to find solutions to issues concerning racetracks, traffic lights, and other similar topics, the L.C.M. concept is essential.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out