The word trigonometry has been derived from the Greek word trigonon, “triangle” and metron, “measure”. So, basically it is the branch of mathematics which deals with the study of the relationship between sides and angles of a right-angled triangle. It is the most practical branch of mathematics and you can see many of its applications in the real world. It is not only limited to mathematics but you can see its application in civil engineering to work out the height of buildings, bridges etc. It is used to describe the motion of objects. To find the trajectory of a bullet fire from a gun-even you can see its applications in physics also. In this particular article we are more focused towards some important topics like: trigonometric identities, reciprocal identities and periodic identities.
What are Trigonometric identities?
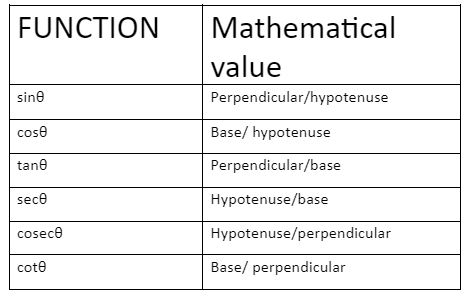
Trigonometric Ratios are expressed as the ratio of hypotenuse, base, perpendicular of a right-angled triangle.
Trigonometric identities are the relationship between trigonometric ratios.
Some basic trigonometric identities.
1) sin2A + cos2B=1
2) 1 + tan2A=sec2A
3) 1 + cos2A=cosec2A
Derivation of trigonometric identities
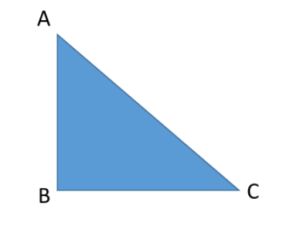
As AC is the longest side and in front of 90° so, it is called hypotenuse = AC.
Take a reference angle at C, the opposite side to this angle is perpendicular = AB
The adjacent one is base = BC.
According to Pythagoras theorem,
AC2 = BC2 + AB2 …… (1)
Divide equation (1) with the square of hypotenuse i.e. AC2
AC2/AC2 = BC2/AC2+ AB2/AC2
1 = (BC/AC)2+ (AB/AC)2 …….(2)
We know that,
sinθ = perpendicular/hypotenuse = AB/AC
and cosθ = base / hypotenuse = BC / AC
Putting these values in equation ( 2).
1 = (cosθ)2+ (sinθ)2
If we rearrange this equation we get,
sin2θ+ cos2 θ = 1
Identity 1 is valid for angles 0 ≤ a ≤ 90.
Now, divide equation (1) with the square of perpendicular i.e. AB2
AC2/AB2 = BC2/AB2 + AB2/AB2
(AC/AB)2 = (BC/AB)2 +1 …… (3)
Again, we know that
cotθ = base/perpendicular = BC/AB
And cosecθ = hypotenuse / perpendicular = AC / AB
Putting values in equation (3).
(cosecθ)2 = (cotθ)2 + 1
If we rearrange this equation we get,
cosec2θ = 1+ cot2θ
As we know, cosec θ and cot θ are not defined for a = 0°, therefore the identity 2 is true for all the values of ‘a’ except at a = 0°. Therefore, it is true for all such that, 0° < a ≤ 90°.
Now, we will divide equation (1) with base i.e. BC2
AC2/BC2 = BC2/BC2 + AB2/BC2
(AC/BC)2 = 1 + (AB/BC)2 ……. (4)
We know that
tanθ = perpendicular / base = AB / BC
and secθ = hypotenuse / base = AC / BC
putting this in equation (4).
(secθ)2 = 1 + (tanθ)2
If we rearrange this equation we get,
sec2θ = 1+ tan2θ
As we know that tan θ is not defined for a = 90° therefore identity 2 obtained above is true for 0 ≤ A <90.
Triangle identities
Triangle identities are not only for right-angled triangles but are applicable for all triangles.
Let ABC be a triangle with sides = a, b, c.
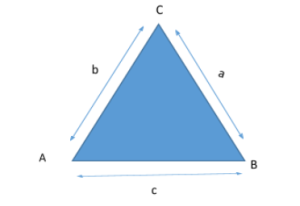
Sine law – it is the ratio of opposite angle to side length.
It is used to find unknown angles and length of a triangle.
a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC
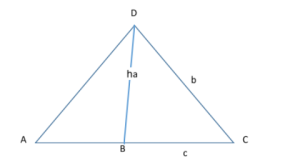
Law of sines proof
Given: △ACD, AC = c, DC = b and AD = a
Draw a perpendicular DB ⊥ AC. Then DB = h is the height of the triangle. “h”.
b/a = Sin A / SinC
To Show: b/a = Sin A / Sin C
Proof: In the △DBA,
Sin A= h/a
And in △DBC,
Sin C = h/b
Therefore, Sin A / Sin C = (h / a) / (h / b)= b/a
Hence proved.
Similarly, we can prove, Sin C/ Sin S= a/ c & any pair of angles and sides.
Cosine law– it states that if the length of two sides and angle between them is given, then we can find the length of the third side.
c2 = a2 + b2 – 2ab
Tangent law– it describes the relationship between sum and difference of a right triangle and tangents of half of the difference and sum of corresponding angles.
Reciprocal identities
These are nothing but reciprocal of sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, cosecant..
These are also known as inverse identities.
To learn reciprocal identities you should have a good grasp on the six standard trigonometric functions.
Each function is reciprocal of another.
sin (θ) = 1 / cosec (θ)
The reciprocal for cosine function is secant function.
cos (θ) = 1 / sec (θ)
The reciprocal for tangent function is cotangent function.
tan (θ) = 1 / cot (θ)
The reciprocal for cosecant function is sine function.
cosec (θ) = 1 / sin (θ)
The reciprocal for secant function is cosine function.
sec (θ) = 1 / cos (θ)
The reciprocal for cotangent function is tangent function.
cot (θ) = 1 / tan (θ)
Periodicity Identities
Periodicity identities states that if we shift the graph of a trigonometric function by one period to the left or right it will not change the function.
The functions of sin, cos, sec, and cosec repeat every 2π units; tan and cot, on the other hand, repeat every π units.
To simplify expressions you can use periodic identities.
. sin(x+2π) = sinx
.cos(x+2π) = cosx
.tan(x+π) = tanx
.cot(x+π) = cotx
.sec(x+2π) = secx
.cosec(x+2π) = cosecx
How to Find the Period of a Function?
Periodic function repeats after a period of time.
It is represented like f(x) = f(x + p), p is the period of a function and it is a real number.
Period means the time interval between the two occurrences of the wave.
Conclusion
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the study of the relationship between angles and sides of a triangle. Trigonometric identities are the basis of trigonometry which can represent each trigonometric ratio to other. It means that if you know the value of any ratio, then you can easily find the missing one. Trigonometry may not include everyday applications, but it helps you to deal with triangles more readily. Reciprocal identities are the reciprocal of basic functions; it is the basic relations between functions. Periodic identities illustrate the function of graphs.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






